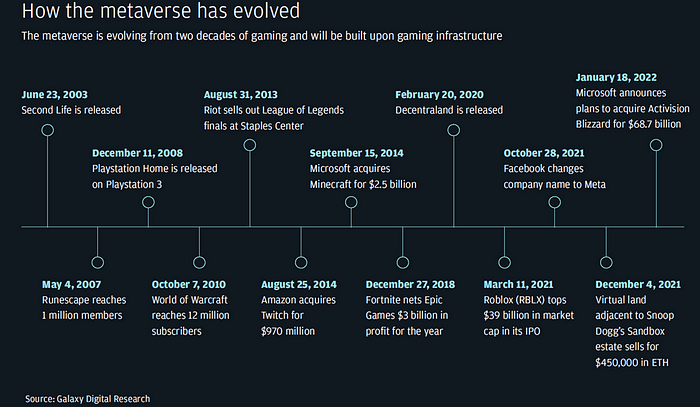
Metaverse: Insights & Opportunities
By Siddharth Khetarpal
What is a Metaverse?
A Metaverse is a collective virtual shared space, created by the convergence of virtually enhanced physical and digital reality. A Metaverse is persistent, providing enhanced immersive experiences.” Gartner expects that a complete Metaverse will be device-independent and will not be owned by a single vendor: It will have a virtual economy of itself, enabled by digital currencies and nonfungible tokens (NFTs).
A Metaverse is an example of combinatorial innovation that requires multiple technologies and trends, such as augmented reality (AR), flexible work styles, head-mounted displays (HMDs), an AR cloud, the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G, artificial intelligence (AI) and spatial technologies, to form a complete Metaverse.
The metaverse will function in essence as an extension of society, the prefix ‘Meta’ means beyond in Greek. Users within the metaverse will be able to interact with others similar to how they interact now, through attending the same concerts, fitness classes or comedy shows with the main discrepancy being that the metaverse will enable such interaction to occur remotely enabling wider interaction Despite the fact that life is returning to normal in many societies, the COVID-19 pandemic has shown people that social interaction can occur remotely, and the adoption of the metaverse has the potential to act as an extension of this.
A Fully Functioning Virtual Economy
Matthew Ball, a tech venture capitalist, has illustrated a framework detailing what a metaverse is, its capabilities and how it differs from our current virtual worlds.
A metaverse, like many incumbent online services, like media streaming, will be ‘always on’, there will be no ‘pause’ or ‘end’, it continues indefinitely.
A metaverse will be synchronous, events, even those pre-scheduled, happen in real time for all connected.
A metaverse will be non-rival in its consumption, one user’s consumption will not diminish the availability of the service for another user, this is also similar to current media streaming and other existing online services.
A metaverse will contain a fully functioning economy, which will enable and facilitate trade between users.
Further, a metaverse will reduce barriers between existing online services. Currently, each online service operates proprietary systems; for example, currency bought in Fortnite cannot be exchanged for an application on the App Store. A metaverse will offer users interoperability where an item purchased in one service can also be utilized in another, for example a Fortnite skin could be equipped during a Counter-Strike session.
Evidently, some of metaverse’s core ideas have been realized within the realm of current technological barriers, however, a Metaverse aims to combine online services that are enjoyed today and provide users a virtual world full of experiences and not simply a list of content to peruse.
What drives the demand/realization of a Metaverse?
The pandemic has increased feasibility of remote interaction
During the pandemic, as social interaction was inhibited through the threat of transmission of COVID-19, many employees who could work from home were often compelled to. While previously remote work had not been particularly widespread, despite the fact that the technology to facilitate remote work has existed for considerable time, the pandemic forced the hands of many, and companies invested heavily in cloud computing services and various other infrastructure to accommodate remote work. This has greatly increased the feasibility for remote work, particularly in advanced, service-based economies. In the UK, for example, McKinsey data finds that a third of work could be completed from home with no reduced productivity. This acceleration towards remote interaction within people’s working lives will help to facilitate the adoption of the metaverse when it becomes feasible.
Metaverse will facilitate work
As seen during the pandemic, remote work has become increasingly viable owing to technological advancements and broadband infrastructure improvements. The metaverse will transform the various software that consumers use into one location and will enable consumers to meet colleagues in a VR 3D space as opposed to the current 2D space facilitated by Zoom and Microsoft Teams etc.
5G will facilitate Virtual Reality growth needed for the metaverse
The COVID-19 pandemic emphasized the importance of connectivity, with consumer use of broadband increasing by two and a half hours per day. Healthcare recorded a 490% increase in telemedicine visits, gaming saw a 75% surge and online transactions were up 74% globally. With the increased usage of broadband worldwide, governments will accelerate the rollout of 5G, as potential use cases increase.
As 5G continues to grow in popularity and availability, both Augmented and Virtual Reality will become increasingly viable for consumers. 5G offers latency of just one millisecond, which should enhance the telepresence capability of existing and future XR headsets. This will also make virtual gaming more feasible as consumers can now stream games on XR headsets using cloud gaming services, bypassing the need for such headsets to contain costly components such as CPU and RAM components.
Low latency speeds, through 5G, will also facilitate virtual entertainment, such as concerts or sporting events. Currently, Fortnite has experimented with virtual concerts, with prominent artists, Marshmello, Travis Scott and Ariana Grande. However, in its current form, synchroneity has been lacking with each user experiencing moments in the concert at slightly different times. With 5G, each user will be able to experience events much more in sync than previously, owing to its ground breaking low latency speeds.
Similarly, when users browse social media sites, each user is connected to the server individually as opposed to other users, which would be enabled through the metaverse.
· One driver of a Metaverse is that people can enhance and/or augment their lives in digital and physical realities:
o Purchasing outfits and accessories for their online avatars (this growing area is referred to as Direct2Avatar)
o Buying digital land and constructing virtual homes
o Participating in a virtual social experience
o Shopping in virtual malls via immersive commerce
o Performing work-related activities in an immersive workplace
o Attending virtual classrooms to experience immersive learning
o Buying digital art, collectibles and assets (NFTs)
o Interacting with digital humans for onboarding employees, customer service, sales and other business interactions
· These activities are taking place in siloed environments (metaverses), but will eventually take place in a single Metaverse.
What drives the demand/realization of a Metaverse?
The pandemic has increased feasibility of remote interaction
During the pandemic, as social interaction was inhibited through the threat of transmission of COVID-19, many employees who could work from home were often compelled to. While previously remote work had not been particularly widespread, despite the fact that the technology to facilitate remote work has existed for considerable time, the pandemic forced the hands of many, and companies invested heavily in cloud computing services and various other infrastructure to accommodate remote work. This has greatly increased the feasibility for remote work, particularly in advanced, service-based economies. In the UK, for example, McKinsey data finds that a third of work could be completed from home with no reduced productivity. This acceleration towards remote interaction within people’s working lives will help to facilitate the adoption of the metaverse when it becomes feasible.
Metaverse will facilitate work
As seen during the pandemic, remote work has become increasingly viable owing to technological advancements and broadband infrastructure improvements. The metaverse will transform the various software that consumers use into one location and will enable consumers to meet colleagues in a VR 3D space as opposed to the current 2D space facilitated by Zoom and Microsoft Teams etc.
5G will facilitate Virtual Reality growth needed for the metaverse
The COVID-19 pandemic emphasized the importance of connectivity, with consumer use of broadband increasing by two and a half hours per day. Healthcare recorded a 490% increase in telemedicine visits, gaming saw a 75% surge and online transactions were up 74% globally. With the increased usage of broadband worldwide, governments will accelerate the rollout of 5G, as potential use cases increase.
As 5G continues to grow in popularity and availability, both Augmented and Virtual Reality will become increasingly viable for consumers. 5G offers latency of just one millisecond, which should enhance the telepresence capability of existing and future XR headsets. This will also make virtual gaming more feasible as consumers can now stream games on XR headsets using cloud gaming services, bypassing the need for such headsets to contain costly components such as CPU and RAM components.
Low latency speeds, through 5G, will also facilitate virtual entertainment, such as concerts or sporting events. Currently, Fortnite has experimented with virtual concerts, with prominent artists, Marshmello, Travis Scott and Ariana Grande. However, in its current form, synchroneity has been lacking with each user experiencing moments in the concert at slightly different times. With 5G, each user will be able to experience events much more in sync than previously, owing to its ground breaking low latency speeds.
Similarly, when users browse social media sites, each user is connected to the server individually as opposed to other users, which would be enabled through the metaverse.
- One driver of a Metaverse is that people can enhance and/or augment their lives in digital and physical realities:
o Purchasing outfits and accessories for their online avatars (this growing area is referred to as Direct2Avatar)
o Buying digital land and constructing virtual homes
o Participating in a virtual social experience
o Shopping in virtual malls via immersive commerce
o Performing work-related activities in an immersive workplace
o Attending virtual classrooms to experience immersive learning
o Buying digital art, collectibles and assets (NFTs)
o Interacting with digital humans for onboarding employees, customer service, sales and other business interactions - These activities are taking place in siloed environments (metaverses), but will eventually take place in a single Metaverse.
• Another goal is to provide innovative new opportunities and business models that enable companies to extend digital business; these opportunities and models will be persistent, decentralized, collaborative and interoperable.
Details
The amount of hype around Metaverse is overwhelming. This hype has been driven by technology companies pre-emptively claiming to be Metaverse companies, or creating a Metaverse.
A Metaverse will consist of many elements and opportunities (see Figure)

A Metaverse will allow people to replicate or enhance their physical activities. This could happen by transporting or extending physical activities to a virtual world or by transforming the physical one. Although the goal of a Metaverse is to combine many of these activities (e.g., Meta’s Horizon and Microsoft’s Metaverse), there are currently many individual metaverses with limited functionality. Table 1 is not exhaustive; however, it lists some of the activities and sample vendors.

Metaverse has been referred to as the next iteration of the internet, which may be a simple, but effective way to at least begin to understand the concepts of a Metaverse. In fact, a Metaverse is also following an evolutionary path similar to that of the internet during the past few decades.
The internet, or more accurately the World Wide Web, started as individual bulletin boards and other online destinations. All of these destinations operated independently. Eventually, these destinations became sites on one united internet. This is similar to how a Metaverse will develop. Today, there are many individual use cases and products, all creating their own version of a metaverse. However, Gartner predicts that, by 2029, they will have combined to form a single, or a limited number of, Metaverse(s), with multiple destinations across multiple technologies and experiences (e.g., phones, tablets, HMDs, AR, MR and VR).
Enterprises will now have the ability to expand and enhance their current businesses in unprecedented ways, opening up opportunities to move from a digital to a Metaverse business. However, the adoption of Metaverse technologies is still nascent and fragmented. Be careful when investing heavily in a specific Metaverse, because it is still too early to determine which investments will be viable in the long term. For example, there has been an increase in investment in virtual real estate. The risk is that virtual real estate may not have any value as Metaverse ecosystems converge into a few or even one Metaverse. We are definitely at a time of learning, exploring and preparing for a Metaverse with limited implementation based on the use cases in Table 1.
Evolution of Metaverse
Deloitte sees the development of Metaverse occuring in 4 stages:
1. Infancy Stage
2. Early Stage
3. Mature Stage
4. Final Stage
Currently, the Metaverse is in its ‘Infancy Stage’ as it many concepts are being proposed around its development. The next 5–10 years are expected to witness the early development of the Metaverse as the relevant technologies mature and the concept of metaverse strengthens.
Moreover, Deloitte has divided the ecosystem of Metaverse into 2 components based on user type:
1. Consumer Metaverse
2. Industrial Metaverse
The figure below lays out the Development Stages:

The infancy stage is from 2016 to 2020. Although the concept of metaverse did not appear, different industries were carrying out technological single-point trials for digitalization or virtualisation. This was the embryo of metaverse:
· In the industrial metaverse, applications were mainly building digital, online and simulation scenarios. For example, Osso VR, a Boston-based doctor training company, has developed software that can create virtual operating rooms to allow doctors to receive more training on complex operations; RaLC, an assembly line simulation software developed by a Japanese AI company, uses 3D animation as the carrier to build simulation verification models for multiple logistics system elements.
· In the consumer metaverse, applications were mainly to facilitate virtual experiences using 2D forms. For example, in the mobile game “Pokémon GO”, jointly developed by Nintendo, The Pokémon Company and Niantic Labs, AR technology is equipped to mobile phones for players to find and capture virtual Pokémon in the physical world; the New York-based health technology company Peloton integrates AR technology with cycling to provide fitness courses on electronic screens, achieving virtual-real integration of 2D imaging and improving users’ immersive experience.
The early development stage is from 2021 to 2030. This stage involves further online, digital and virtual applications and technological advancements in different industries, eventually forming a single-scenario based on independent metaverses and small decentralized, single-industry, multi-centered ecosystems of the metaverse. Technological patterns, platform infrastructure and key connecting devices, such as XR devices, will be primarily developed in this stage. Looking at application developments, the focus will be on the applications in hot industries.
· In the industrial metaverse, the focus will be on the application of basic technologies, which are expected to be expanded to entire-industrial chain and whole-industry virtual applications. For example, NVIDIA actively deploys basic technologies such as virtual 3D simulation and rendering, and applies them to industrial design. At present, the virtual collaboration platforms that can be built through Universal Scene Description technology are mainly applied to digital collaboration and real-time simulation scenarios, creating the technological foundation for the future expansion of metaverse in the industrial design field.
· In the consumer metaverse, the virtual experiences of various independent IPs will deepen. Hardware devices connecting the physical and virtual worlds are continually being developed and optimized. Virtual experiences are improving to provide a greater sense of reality, and a virtual social system is gradually being built. For example, in Roblox, players can exchange game currency with real currency to realize actual economic exchange between virtual and physical worlds. It also provides multiple forms of social interaction to allow users to have a better immersive experience and stimulate their innovative thinking via long online social interactions.
The mature stage starts from 2031, during which the independent metaverses of different industries gradually share data and form unified standards, and achieve integration. Deloitte believes that in this stage, there will be cross-platform and cross-industry ecological connection and integration — the small decentralized, multi-center ecosystems will integrate to gradually form two metaverse ecosystems respectively centering on industries and individuals. Deloitte believes that unified data standards, payment systems and identity authentication are the key to achieving cross-platform development and integration at this stage
· In the industrial metaverse, the independent metaverses of similar industries are expected to gradually share data and industry standards will trend towards multi-industry interactions and integration. For example, the industrial Internet in different industrial fields might gradually develop unified data standards and combine to form an industrial metaverse; smart communities, smart buildings and smart transportation may gradually develop unified data standards and join together to form a smart city metaverse.
· In the consumer metaverse, the virtual experience of independent IPs will no longer be separate. The multiple scenarios and virtual elements in individuals’ virtual lives are connected to build comprehensive virtual life scenarios and content. Thus the virtual assets and information on various platforms are distributed and shared. For example, Marvel heroes, such as Sun Wukong, and virtual concerts by K-pop groups could appear in the same virtual space
Underlying Technologies That Power The Metaverse
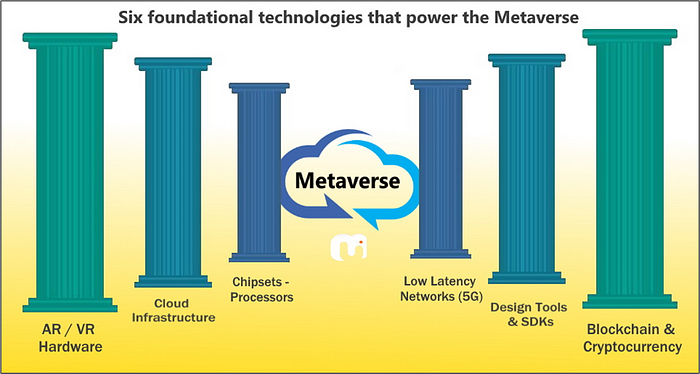
1. AR / VR Hardware
The Metaverse is defined by its immersive experience for its users, and this wouldn’t be possible without AR and VR. At the core, it is all about connected VR experiences that every tech company tries to offer in the metaverse. Imagine that you will be able to walk into a shopping mall, interact with your friends, and have fun with an immersive connected VR just like the way you do in the physical world.
This tier includes a range of hardware devices that will allow users to experience the metaverse. VR Headsets, Touch sensitive Gloves, hologram 3D projectors, Smart glasses (AR) etc.
Today Metaverse focused hardware like virtual reality (VR) headsets and augmented reality (AR) glasses — are being designed to support intense workloads related to high-end graphics and artificial intelligence (AI) on smaller, lightweight devices.
1. Chipsets / Processors
This tier is all about the computing power. Next gen chipsets will support the intense computing and processing requirements of metaverse applications. Chip manufacturers like Qualcomm and Intel have promised huge investments to support the metaverse hardware. Intel claims that the metaverse will necessitate a 1000x increase in computational efficiency, including advancements in 5G and hybrid edge-cloud infrastructures. Qualcomm chipsets are already popular and being used in over 50+ AR/VR devices.
2. Low Latency Networks (5G)
This tier is the lifeline of the metaverse. Wireless technologies that power the high resolution metaverse applications — for immersive virtual worlds or gaming. We will need reliable, ultra-fast, low latency networks to enable the connected VR experience. 5G is considered one of the foundational building blocks for Metaverse. Most of the leading telecom companies started investing to offer 5G network infrastructure. Companies like Verizon, and AT&T have partnered with VR gaming companies to experiment on their 5G network.
3. Cloud Infrastructure
It is obvious that metaverse applications would require highly scalable infrastructure that includes enormous amount of compute, storage, bandwidth and more. Especially for those companies hosting the virtual worlds and experiences. Cloud infrastructure will enable metaverse companies, to process, store and consume the vast amounts of data they generate. Some of the high-profile gaming companies host their infrastructure on cloud. Example: Epic Games host their entire infrastructure on AWS cloud for their popular game Fortnite.
EDGE Computing will be used for metaverse applications that depend on real-time responses, such as AR/VR and gaming. Edge computing will enable data to be processed closer to where it is been created. This helps in situations where data needs to be processed in real time like sensor data from trackers in VR headsets. Edge computing is still a part of the larger cloud infrastructure, while it takes care of specific requirements that needs very quick response.
4. Design Tools & SDKs
3D modeling design tools, SDKs, and AR/VR developer kits will constitute one of the core building blocks of the metaverse.
Companies offer 3D design engines and animated visual effect tools that designers can use to build the visual elements of the metaverse. These engines enable real time generation of 3D graphics (unlike the pre-rendered animation that appears in movies) Examples are:
Unreal Engine and Unity. Most of the 3D game studio companies use one of these 3D design engines today.
3D Model capture tools — helps capture and create 3D representations of physical world products or environments. These tools will enable companies to quickly create metaverse versions of real-life products. For e.g., Vntana uses 3D scanning to transform products like furniture or jewellery into 3D images. PreVu3D creates virtual models of physical spaces (like factories).
Companies offer AR software development kits (SDKs) to enable developers to create, manage and optimize AR app development. Some of the top gaming companies already announced the launch of their AR developer platforms.
After all, developing for the metaverse is going to be different from developing traditional web-based applications for the internet. Because users will interact with the metaverse via specially designed hardware devices. This space is in its infancy, and you can expect more to evolve with a wide range of new platforms and SDKs in the years to come.
5. Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
As the Metaverse evolves, the virtual worlds will need its economic infrastructure layer to be built. The foundation for this is already set. Blockchain and crypto currencies are being widely adapted as the foundation for the economic infrastructure in the metaverse. This will enable people to buy, sell, and store goods and services in the metaverse.
Ideally, PAYMENTS become an essential part of the metaverse ecosystem. As the economies in the virtual world grow, users will adapt typical online payment systems that emerge out of blockchain and cryptocurrency ecosystem. Of course, the metaverse would run on a decentralized financial infrastructure with blockchain as its foundation.
CRYPTO EXCHANGES will enable you to buy and sell cryptocurrencies that can be used in various virtual worlds. Crypto exchanges and crypto currencies are widely adapted and already in use. Companies like Binance, Gemini and Crypto.com allows you to trade crypto
currencies today. Crypto currencies like MANA, SAND can be purchased / traded on multiple platforms.
NON-FUNGIBLE TOKENS (NFTs) will be another form of asset that you buy and trade in the metaverse. There are NFT marketplaces (like Sandbox, Open sea, Rarible, Axie) where you can buy and sell NFTs of everything from virtual land to avatar clothing to virtual buildings in the decentralized worlds. NFTs will become the primary form factor to purchase and hold your metaverse based assets/property.
XR (Extended Reality) which is comprised of Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality and Mixed Reality is the entrance for exploring the metaverse: XR devices are the key equipment connecting the virtual and real worlds. At the early development stage, the priority is to construct and develop infrastructure and equipment. Currently, we need to develop the key products, i.e. XR devices, and apply their basic functions.
According to Jon Radoff (founder of live game services platform Beamable), who proposed seven layers of the metaverse, the realization of the metaverse consists of seven layers of development and implementation. The infrastructure and human interface layers are mainly for deployment of hardware, software and other infrastructure and equipment. The decentralization and spatial computing layers are for the deployment of development tools. The creator economy, discovery, and experience layers are for the deployment of application products and operational ecosystems.
Based on the four development stages of the metaverse, the focus in the early development stage will be put on infrastructure and equipment as well as development tools. The infrastructure and equipment, in particular, constitute the basic technical framework and key equipment for the construction of metaverse ecosystems.
The development level of XR equipment-related technologies is expected to meet the current development needs of the metaverse.
As per the ‘six core technologies of the metaverse’, and the four development stages of the metaverse identified as above, the development level of the relevant XR technological reserve satisfies the application and product needs of the early development stage of the metaverse.
XR devices are the key connecting devices of the metaverse ecosystems. They have different characteristics than the mobile Internet, such as three-dimensionality, natural interaction and spatial computing. At present, the metaverse is still confined to two-dimension worlds, with a large gap compared to real three-dimensional immersive experience. XR devices will facilitate the virtual-physical connection necessary for realizing the metaverse, and will be the key to engaging users
Figure: The Seven Layers Of Metaverse

Market Size, Economics & Opportunities
The Metaverse is expected to be a trillion-dollar revenue opportunity across advertising, social commerce, digital events, hardware, and developer/creator monetization.
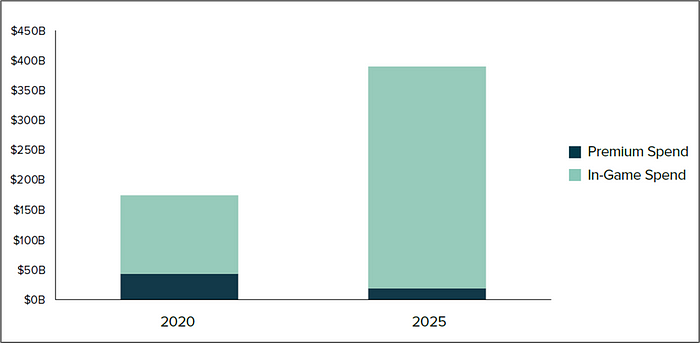
Social lives and gaming are converging and creating a large, fast-growing virtual goods consumer economy. It is estimated that revenue from virtual gaming worlds could grow from ~$180 billion in 2020 to ~$400 billion in 2025.
The continued shift of game developer monetization is a key dynamic within this growth trend. Players are increasingly moving away from paying to play premium games towards free games, which developers monetize by selling players in-game items to enhance gameplay or social status within these virtual worlds.
Global Virtual World Revenue Growth
This shift is accelerating further with the transition from Web 2.0 closed corporate metaverses to Web 3.0 open crypto metaverse networks, which are:
· Web 2.0 Closed Corporate Metaverse: centrally owned and controlled by big tech, or;
· Web 3.0 Open Crypto Metaverse: democratically owned and controlled by global users.
Many gamers today spend their money and hours of their time building digital wealth within Web 2.0 closed corporate metaverse worlds. The problem is, most game developers don’t let players monetize their investment and efforts. Developers prohibit players from trading items with other players and keep these worlds closed so players cannot transfer their in-game wealth to the real economy. Web 3.0 open crypto metaverse networks solve this problem by eliminating the capital controls imposed on these virtual worlds by Web 2.0 platforms. This
new paradigm allows users to own their digital assets as Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), trade them with others in the game, and carry them to other digital experiences, creating an entirely
new free-market internet-native economy that can be monetized in the physical world. This evolution of the “creator economy” is known as “Play to Earn”.

In the metaverse, users dictate these types of seamless, real-world adjacent interactions across digital communities. Conversely, the closed nature of Web 2.0 corporate Metaverse platforms may put users at a disadvantage compared to Web 3.0 open crypto Metaverse networks. Established Web 2.0 corporations will need to disrupt their business models by opening up their ecosystems and removing their competitive moats. We don’t yet know the path Facebook will take with their Metaverse ambitions, but they — like other Web 2.0 companies — will need to make this challenging shift in the face of pressure to meet quarterly results for shareholders. Gaming is just one of the most immediately addressable segments where value is already starting to naturally shift to Web 3.0, but the Metaverse opportunity extends far beyond gaming.

The total market cap of the leading Web 3.0 Metaverse crypto networks sits at ~$27.5 billion. This pales in comparison to the ~$900 billion market cap of Facebook, the ~$2 trillion market cap of the gaming sector, and the $14.8 trillion market cap of Web 2.0 companies that could shift to the Metaverse or risk disruption.

METANOMICS: The Metaverse Economics
Web 3.0 crypto Metaverses are emerging market virtual world economies with a continually developing complex mix of digital goods, services, and assets that generates real-world value for users. Early Web 3.0 metaverse worlds have been typically built on top of blockchain computing platforms (layer one) with a host of parties contributing to the development of the games and in-games items that can be freely traded on the blockchain.

Users purchasing these items are starting to build a new e-commerce experience. Examples of some more popular business activities within Decentraland and other virtual world economies today are:
· Art Galleries, such as Sotheby’s, have launched allowing owners to showcase and sell their digital NFT art at auction.
· Business Offices: crypto businesses like Binance and others have established digital headquarters in the Metaverse where employees can meet and collaborate.
· Games & Casinos where players can win MANA.
· Advertising: digital billboards have been built by property owners to advertise to game players for a fee.
· Sponsored Content, such as the recently announced Atari arcade which will feature games that can be played within Decentraland.
· Music Venues where DJs and musicians play music and hold concerts
These Web 3.0 Metaverse worlds are part of a larger interconnected crypto cloud economy. These decentralized protocols interoperate with and provide the technical infrastructure to support Metaverse virtual economies.
· Payment: Web 3.0 metaverse economies can use their own digital currency, like MANA, or the currency of the layer one base crypto cloud economy platform they’re built on, such as Ethereum (ETH) or Solana (SOL).
· Decentralized Finance: Decentralized exchanges allow users to trade in-game items while lending platforms allow users to take out loans on their virtual land.
· NFT Sovereign Goods: Players can purchase NFTs from other creators and bring them into other virtual worlds to be put on display or sold.
· Decentralized Governance: Legal frameworks take back control of the digital economies from centralized corporations and allow a global network of Web 3.0 metaverse users to decide the rules of their collectively owned virtual space.
· Decentralized Cloud: File storage solutions such as Filecoin give Web 3.0 metaverse worlds a decentralized infrastructure solution to store data while services like Livepeer give virtual worlds decentralized video transcoding infrastructure.
· Self-Sovereign Identity: Internet-native social reputation coin (“creator coins”) data from other platforms may be transferred into the Metaverse and used for identity or credit scoring.

Meta Web 3.0 Metrics
The combination of these innovations has created a new online experience that’s already attracting users. Web 3.0 Metaverse virtual world users have seen rapid growth over recent years. Today, Web 3.0 Metaverse virtual worlds have nearly 50,000 all-time users (active wallets as proxy), up ~10x since the beginning of 2020

Compared to other Web 3.0 and Web 2.0 segments, Metaverse virtual world users are still in their early innings, but if current growth rates remain on their current trajectory, this emerging segment has the potential to become mainstream in the coming years.

Web 3.0 Metaverse virtual worlds are creating real-world value for the developers, third-party creators, and users building these emerging market internet-native crypto cloud economies. All-time value spent on Web 3.0 Metaverse item sales such as virtual land, goods, and services has topped $200 million.
By removing the Web 2.0 centralized companies that have historically controlled these online spaces, Web 3.0 Metaverse virtual worlds have benefited from rapid innovation and productivity gains.
Crypto virtual worlds have created a multi-million dollar primary and secondary market for creators and asset owners by eliminating capital controls and opening their digital borders to free market capitalism.

During Q3 of 2021, total crypto fundraising totalled $8.2 billion with the Web 3.0 & NFT segment comprising $1.8 billion. Within the Web 3.0 & NFT sector, blockchain based gaming attracted ~$1 billion in funding across 14 deals, ranking it the top subsector within the category.

Capital investment into the sector has recently started to accelerate but compared to the $10 billion that companies like Facebook plan to invest, and the amounts that could follow from other companies and venture capitalists, the Metaverse is in its early innings.
Bibliography:
1. Deloitte China, Metaverse Report — Future is here — Global XR Industry Insight, March 2022
2. J.P.Morgan, Opportunities in the metaverse — How businesses can explore the metaverse and navigate the hype vs. reality, 2022
3. Grayscale Research, The Metaverse — Web 3.0 Virtual Cloud Economies, November 2021
4. MarketLine Analyst Insights, Big Tech back the Metaverse — Strong Investment Expected in 2022, January 2022
5. MarketLine Analyst Insights, Facebook Plans to Create Metaverse — Zuckerberg outlines ambitions for new initiative, August 2021
6. MarketLine Analyst Insights, Facebook — Generation Z and data privacy are the platform’s existential treats, February 2022
